
01 Nov, 2025
Compared to the pneumatic tires that can be seen everywhere in life, solid tires do not stand in the spotlight. However, solid tire is still an infrequent but important member of the whole tire family.
Definition: According to Wikipedia, solid tires, also named airless tires, are tires that are not supported by air pressure. It is manufactured using layers of rubber that are constructed around a metal frame or a wheel structure that can be mounted to a specific vehicle. They can also be made to fit on rims that are manufactured to support pneumatic tires.
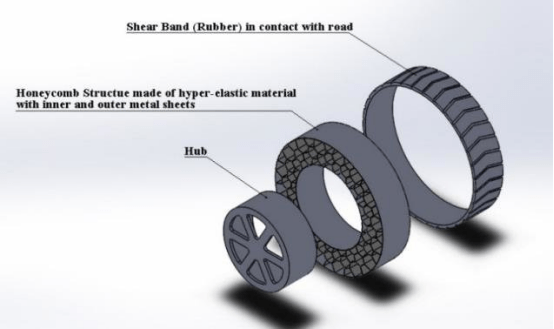
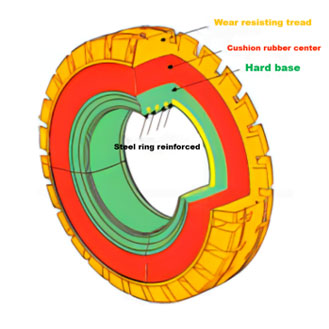
Solid tires serves in a variety of applications. Most solid tires are used in industrial applications for large tractors and trucks that are prone to road and ground hazards. These machines are typically used in construction areas where various metals, scrap, nails, screws, and other hardware may often pierce the tires of heavy-duty vehicles. Recycling centers and landfills utilize solid tires to transport large amounts of material and traverse many ground-level hazards.
Solid tires can also be used for smaller devices. Forklifts use solid tires to maintain stability and the ability to transport heavy loads. Even smaller applications include bicycle tires and lawn mower tires. Solid tires are also placed on castors and are used in many different applications from furniture to movie camera carts.
Here are some specific application examples:




As the first tire in history, solid tires are still used, indicating that it has advantages that cannot be ignored compared to pneumatic tires.
But why can’t solid tires with such advantages replace pneumatic tires? Just as everything is a double-edged sword, solid tires have their drawbacks and limits.
There are different classification criteria for solid tires.
According to the structure, solid tires are generally divided into two types – bonded type and non-bonded type.
The former refers to tires where rubber is directly vulcanized on the rim, and the latter refers to tires that are fixed on the rim after vulcanization.


According to the use, solid tires are divided into anti-static, oil-resistant, high-load solid tires, environmentally friendly solid tires, etc
According to the different vehicles applied, solid tires can be divided into solid skid steer tires, solid scissor lift tires, solid boom lift tires, solid telescopic arm forklift tires, solid wheel loader tires, solid underground tires…
According to the working Environment, except the general tire, there is a non-marking solid tire which is used in many fields that demands high levels of hygiene. In these situations, tires are required to leave no or less tire marks in the process of using and so that the ground is able to maintain clean. The light-colored rubber formula avoids leaving black marks and braking trace on the ground during driving. That’s the reason why the colors of this kind of tire are mostly white, gray, green, yellow, etc.



There are some common sizes of solid tire as following shows,
| 4.00-8 | 5.00-8 | 6.00-9 | 6.50-10 | 7.00-9 | 7.00-12 | 7.00-15 |
| 7.50-15 | 7.50-16 | 7.50-20 | 800-16 | 28×9-15 | 825-12 | 825-20 |
| 9.00-16 | 9.00-20 | 10.00-20 | 11.00-20 | 12.00-20 | 12.00-24 | 14.00-24 |
| 250×15 | 300×15 | 15×4 1/2-8 | 16×5-9 | 16×6-8 | 18×7-8 | 21×8-9 |
| 23×9-10 | 27×10-12 | 200/50-10 | 17.5-25 | 23.5-25 | 31x6x10 | 33x6x11 |
Here comes a question —- How to read sizes of solid tire?
There are two type regarding of solid sizes.They are composed of two groups and three groups.

As above photo shows, size of this tire is 8.25-15
Group one: 8.25 It refers to the nominal section width in inches
Group two: 15 It refers to diameter of the rim in inches
As above photo shows, size of this tire is 23×10-12
Group one: 23 It refers to the overall diameter in inches
Group two: 10 It refers to the nominal section width in inches
Group three: 12 It refers to diameter of the rim in inches

Solid tires have higher quality requirements. That’s why extra care needs to be taken before decision-making.Generally speaking, the quality of solid tires is determined by raw materials and production technology.
The main stream manufacturers almost share the same technology, so the key point lies in the raw materials. At present, there are three kinds of solid tire raw materials, they are:
For tires made of the first raw material (natural rubber imported from Southeast Asia), they show excellent heat resistance and excellent long-lasting working ability. Generally, this tire can work for totally 8 hours.
For tires made from the second and third raw materials, they are more likely to heat up against the ground, resulting in shorter single-day use – only 1-3 hours per day.
Therefore, it is necessary to figure out the raw materials before placing an order.



Solid tires should not be directly exposed to sunlight, and should be kept away from harmful substances such as light, heat, grease, acid and alkali. Besides, it is recommended to place them horizontally. If we put them upright, it is easy for them to overturn and might result in injuries.

As vehicle cabins become quieter, tire noise has become one of the main sources of unwanted sound, especially at medium and high speeds. Noise-reducing tires are developed to address this issue directly at the tire–road interface, where most road noise is generated. Decibel scale: from quiet to road noise (Source: Continental) Where Tire Noise Comes FromFrom […]
Discover More
This research strives to enhance the safety of multi-piece wheel assemblies as injuries and fatalities are associated with their failure, yet information on this topic is limited.Experiments were performed to determine mechanical performance and planar deformation characteristics of several tires to aid in numerical model development. For a 29.5-29 tire, observations included determining vertical versus […]
Discover More